The proper use of headings on a website’s homepage plays an important role in both enhancing user engagement and optimising your site for search.
Headings help readers and search engines to understand what your site is about, what is important and how your content is all connected.
Headings provide structure. They act as signposts on a user’s visual journey down a web page. They inform and introduce content, allowing a user to easily and quickly digest what your site is about and to navigate to the areas they want to read.
Remember that users scan web pages rather than read them. So presenting your content in an organised and structured format caters to the needs of your audience.
A common mistake made when building a website homepage, is incorporating long blocks of text with no headings. This is not a good user experience.
When a visitor lands on a homepage, they want to quickly determine if they should invest time on that page. Studies show that you have no more than 15 seconds to convince a visitor before they bounce. Informative and descriptive headings can help persuade a visitor that your site is worth a longer look.
What is a heading
Headings are the HTML ‘tags’ used to create structure on a web page. You’ll find them in the content management system of your website - typically within the Format menu of the editor.
There are six levels of headings, from H1 (the most important) to H6 (the least important). The most common headings are H1, H2, and H3 tags.
In the page’s source code, a heading tag will look like this: <h1></h1>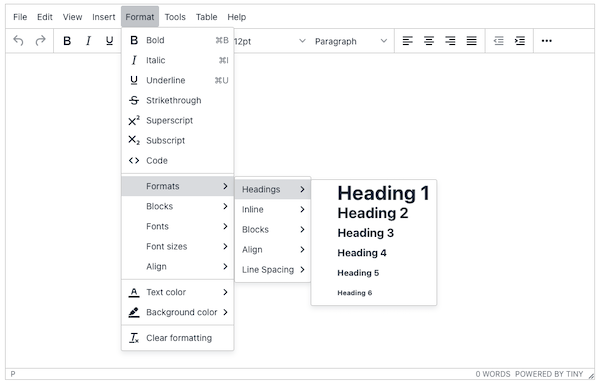
How to use headings to format a web page
Headings reveal a web page’s hierarchy. Heading 1 is most important.
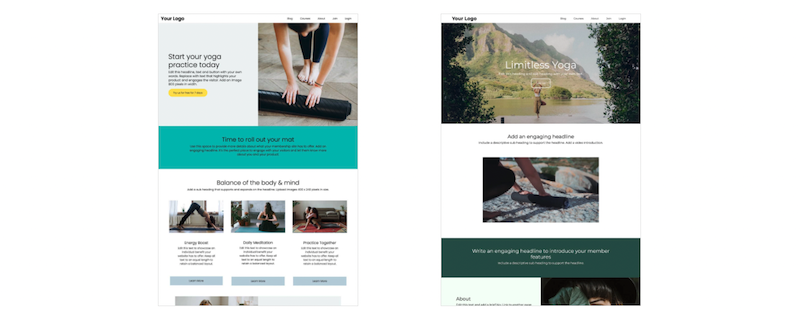
On a website’s homepage, heading 1 is reserved for use only in the headline text of the banner or hero image. It should be between 20 - 70 characters in length and visually striking - meaning make it big and bold. The intention of a bold H1 heading is to influence the interaction between the user and your web page. You want to grab a reader’s attention.
Google tracks the number of visitors that come to your page and 'bounce' without viewing any other pages. A high 'bounce rate' can have a negative impact on your SEO.
Bold, engaging and informative headings can persuade visitors to click more links on your site.
Throughout the rest of your site, the H1 heading should only be used once on each web page. For example, on a blog post, it should only be used in the title.
Using the H1 heading more than once on a page dilutes its impact.
The H2 heading should be used to separate a page into sections. Use H3 headings to cover topics within those sections. Ordinarily you don’t need to use headings beyond H3 unless the page’s content is complex or technical.
Best practice for writing a good headline
Use headings to organize your thoughts as well as your website's content. Your headings should be concise, informative and descriptive. They should relate to the content beneath them. Use them sparingly so that you don't overwhelm the reader with too much information.
Headings & SEO
Headings communicate what your content is about. They strengthen your site by making it easier for people and bots to understand the content and context of your web pages.
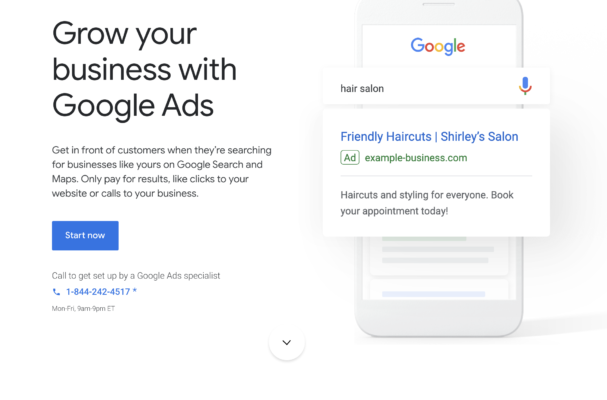
Employing your important keywords and phrases in your headings also plays a significant role in boosting your SEO impact. Their inclusion provides another opportunity for Google and other search bots to accurately interpret what your website is about and deliver it in the results for search queries relevant to its content.
Conclusion
Headings are a powerful tool in web page design. Take advantage of their ability to create structure for your web page, provide focus for your reader and positively impact your SEO performance.